How to Make an All-direction Vehicle With Mecanum Wheels
by Makeblock Robotics in Circuits > Arduino
52550 Views, 472 Favorites, 0 Comments
How to Make an All-direction Vehicle With Mecanum Wheels


The all-direction vehicle is equipped with four Mecanum wheels. The cool part of this vehicle is the flexibility of moving in any direction while keeping itself in a constant direction. It is achieved with the special structure of Mecanum wheel and their proper configuration on the vehicle. You can visit the website and download the omndirectional.pdf file to get to know how it works. In general, the speeds of Mecanum wheel are governed by the equations in the above picture.
So, let’s build a real one from assembling its framework.
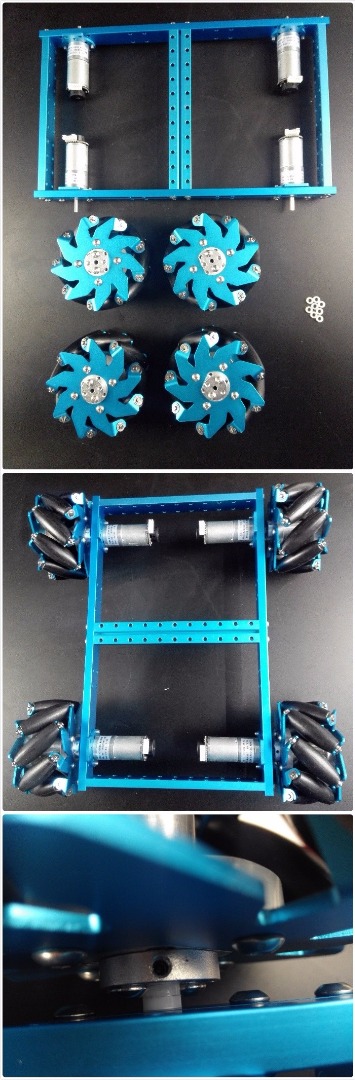
Assemble Rectangle Framework

Assemble rectangle framework with beams and screws from Makeblock.
Assemble Encoder Motors

The speed of four Mecanum wheel is dependent on the speed of vehicle, therefore, it should be precisely controlled to avoid wheel sliding. Encoder motors are used to achieve this goal.
Install Motors on the Framework

Install Mecanum Wheels
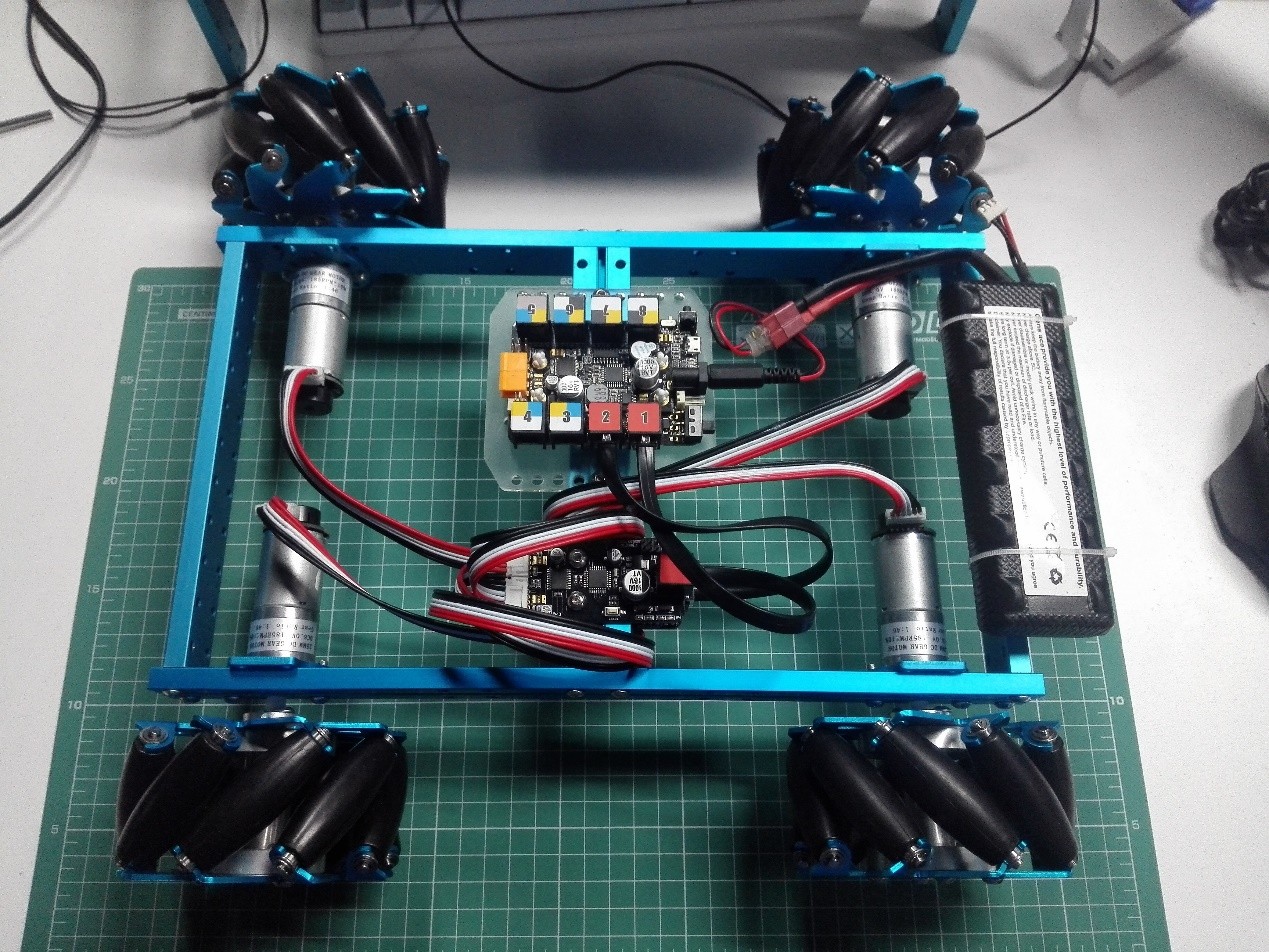
Wiring

An encoder motor driver from Makeblock is able to drive two encoder motors. Two encoder motor drivers are enough for this vehicle. They are connected to port 1 and port 2 on the Orion board respectively. Please keep consistent between wiring and defining ports in your codes.
Install a Battery

The framework of all-direction vehicle with Mecanum wheels is shown in the figure above.
Programming


The speed of four Mecanum wheels are determined by the angular velocity
and speeds in x-axis and y-axis of the vehicle. A Joystick is used to control the speed of the platform with left stick for translatory velocity, and right stick for angular velocity. Plug a Me USB Host module into port 3 of Orion board and then plug a wireless module into Me USB Host module.
Download Makeblock library and put it under Arduino library. The Arduino codes are as follows:
#include "Wire.h"
#include "SoftwareSerial.h"
#include "MeOrion.h"
MeUSBHost joypad(PORT_3);
MeEncoderMotor motor1(0x02, SLOT2);
MeEncoderMotor motor2(0x02, SLOT1);
MeEncoderMotor motor3(0x0A, SLOT2);
MeEncoderMotor motor4(0x0A, SLOT1);
float linearSpeed = 100;
float angularSpeed = 100;
float maxLinearSpeed = 200;
float maxAngularSpeed = 200;
float minLinearSpeed = 30;
float minAngularSpeed = 30;
void setup()
{
motor1.begin();
motor2.begin();
motor3.begin();
motor4.begin();
Serial.begin(57600);
joypad.init(USB1_0);
}
void loop()
{
Serial.println("loop:");
//setEachMotorSpeed(100, 50, 50, 100);
if(!joypad.device_online)
{
Serial.println("Device offline.");
joypad.probeDevice();
delay(1000);
}
else
{
int len = joypad.host_recv();
parseJoystick(joypad.RECV_BUFFER);
delay(5);
}
//delay(500);
}
void setEachMotorSpeed(float speed1, float speed2, float speed3, float speed4)
{
motor1.runSpeed(speed1);
motor2.runSpeed(-speed2);
motor3.runSpeed(-speed3);
motor4.runSpeed(-speed4);
}
void parseJoystick(unsigned char *buf) //Analytic function, print 8 bytes from USB Host
{
// debug joystick
// int i = 0;
// for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
// {
// Serial.print(buf[i]);
// Serial.print('-');
// }
// Serial.println(buf[7]);
// delay(10);
// increase and decrease speed
switch (buf[5])
{
case 1:
linearSpeed += 5;
if (linearSpeed > maxLinearSpeed)
{
linearSpeed = maxLinearSpeed;
}
break;
case 2:
angularSpeed += 5;
if (angularSpeed > maxAngularSpeed)
{
angularSpeed = maxAngularSpeed;
}
break;
case 4:
linearSpeed -= 5;
if (linearSpeed < minLinearSpeed)
{
linearSpeed = minLinearSpeed;
}
break;
case 8:
angularSpeed -= 5;
if (angularSpeed < minAngularSpeed)
{
angularSpeed = minAngularSpeed;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
if ((128 != buf[0]) || (127 != buf[1]) || (128 != buf[2]) || (127 != buf[3]))
{
float x = ((float)(buf[2]) - 127) / 128;
float y = (127 - (float)(buf[3])) / 128;
float a = (127 - (float)(buf[0])) / 128;
mecanumRun(x * linearSpeed, y * linearSpeed, a * angularSpeed);
}
else
{
switch (buf[4])
{
case 0:
mecanumRun(0, linearSpeed, 0);
break;
case 4:
mecanumRun(0, -linearSpeed, 0);
break;
case 6:
mecanumRun(-linearSpeed, 0, 0);
break;
case 2:
mecanumRun(linearSpeed, 0, 0);
break;
case 7:
mecanumRun(-linearSpeed / 2, linearSpeed / 2, 0);
break;
case 5:
mecanumRun(-linearSpeed / 2, -linearSpeed / 2, 0);
break;
case 1:
mecanumRun(linearSpeed / 2, linearSpeed / 2, 0);
break;
case 3:
mecanumRun(linearSpeed / 2, -linearSpeed / 2, 0);
break;
default:
mecanumRun(0, 0, 0);
break;
}
}
}
void mecanumRun(float xSpeed, float ySpeed, float aSpeed)
{
float speed1 = ySpeed - xSpeed + aSpeed;
float speed2 = ySpeed + xSpeed - aSpeed;
float speed3 = ySpeed - xSpeed - aSpeed;
float speed4 = ySpeed + xSpeed + aSpeed;
float max = speed1;
if (max < speed2) max = speed2;
if (max < speed3) max = speed3;
if (max < speed4) max = speed4;
if (max > maxLinearSpeed)
{
speed1 = speed1 / max * maxLinearSpeed;
speed2 = speed2 / max * maxLinearSpeed;
speed3 = speed3 / max * maxLinearSpeed;
speed4 = speed4 / max * maxLinearSpeed;
}
setEachMotorSpeed(speed1, speed2, speed3, speed4);
}Upload Codes to Orion Board and Have Fun
Upload codes with Arduino IDE, you are ready to play with this cool vehicle.