Master-Slave Communication Between Arduino Boards Using HC-05 Bluetooth Modules
by Rachana Jain in Circuits > Arduino
747 Views, 2 Favorites, 0 Comments
Master-Slave Communication Between Arduino Boards Using HC-05 Bluetooth Modules

Bluetooth communication is a popular method for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. In this instructable, we’ll demonstrate how to configure two HC-05 Bluetooth modules as master and slave and establish communication between two Arduino boards.
This tutorial includes:
- Configuring HC-05 modules using AT commands
- Wiring diagrams for master and slave circuits
- Arduino codes for master and slave boards
- Step-by-step explanation of master-slave communication
Supplies
2 x Arduino UNO boards
2 x HC-05 Bluetooth modules
2 x Breadboards
Jumper wires
4 x1k and 2k resistors
12V Supply Adapter
DC Fan
3 Push Buttons
Configuring the HC-05 Bluetooth Modules Using AT Commands
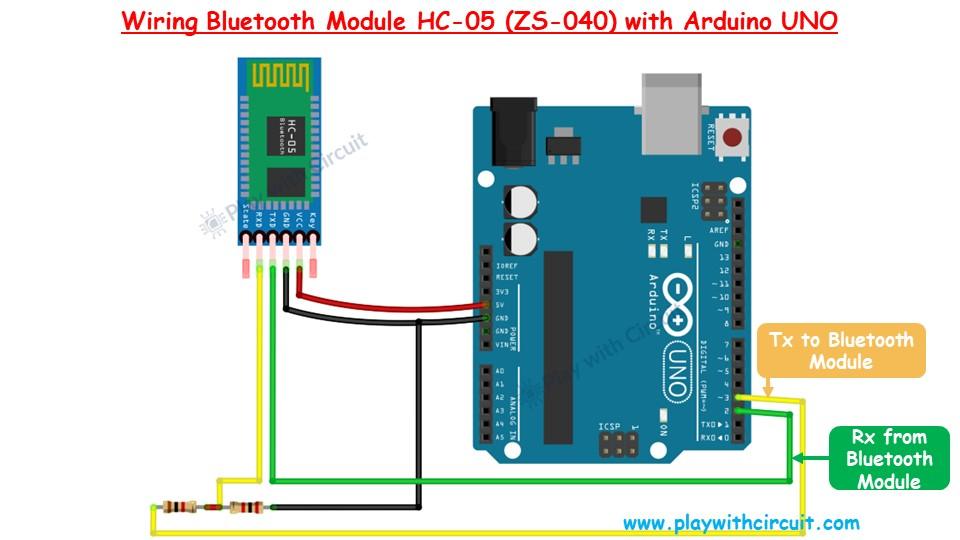
To configure the HC-05 Bluetooth modules, we first need to connect them to a PC via an Arduino board and use the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE to send AT commands. The connection setup between the HC-05 module and Arduino UNO is shown in image.
The HC-05 module communicates through a serial UART interface, but Arduino UNO's built-in serial interface is used for uploading code. To resolve this, we reassign Arduino pins 2 and 3 as software-based Tx and Rx communication lines.
Voltage Level Conversion for HC-05 Rx Pin
The Rx pin of the HC-05 module is not 5V tolerant, so a voltage divider circuit is used to step down the voltage to 3.3V. This is achieved using two resistors (1kΩ and 2kΩ) in the following manner:
- Connect a 1kΩ resistor and a 2kΩ resistor in series.
- The junction of the resistors outputs 3.3V, suitable for the Rx pin of the HC-05.
The module’s Vcc and Gnd pins are connected to the 5V and Gnd pins of the Arduino, respectively.
Code
This code facilitates communication with Bluetooth Module HC-05 and we will be able to configure the Bluetooth module using Arduino’s Serial Monitor.
To ensure this code functions correctly, follow these steps to put the Bluetooth module into Command Mode:
- Press and hold the button located on the Bluetooth module above the EN (Enable) pin before powering up the module.
- While continuing to hold the button, power on the module.
- Keep the button pressed for at least 2 seconds after powering up, then release it.
Putting Bluetooth Module in Command Mode
To assign the HC-05 Bluetooth module a specific role (Slave or Master), it must first be put into Command Mode to accept AT commands. Follow these steps carefully:
Step 1: Wire the Bluetooth Module
Connect the HC-05 module to the Arduino UNO as per the circuit diagram. Ensure proper connections, including the voltage divider for the module's Rx pin, and upload the code to the Arduino.
Step 2: Disconnect the USB Cable
Once the code is successfully uploaded, disconnect the USB cable from the Laptop/PC to ensure the Arduino restarts properly during the next steps.
Step 3: Configure the Serial Monitor Settings
- Open the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.
- Set the baud rate to 9600,n,8,1 (9600 baud rate, no parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit).
- Choose the "Both NL & CR" option for Line Ending.
Step 4: Press the Button on the Bluetooth Module
- Hold down the button on the HC-05 module (located above the Enable pin).
- While holding the button, reconnect the USB cable to the Laptop/PC to power the Arduino.
Step 5: Wait for Confirmation
Keep the button pressed until a message appears in the Serial Monitor indicating that the module is in Command Mode.
This confirms that the module is ready to receive AT commands for configuring its role as Master or Slave.
Configuring the Bluetooth Module for the Slave Role
Once the HC-05 module successfully enters Command Mode, follow these steps to configure it as a Slave:
Step 1: Test Communication
- Open the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.
- Type AT and press Enter.
- The module should respond with OK, indicating successful communication between the module and the Arduino.
Step 2: Change the Module Name
- To rename the module, type: AT+NAME=SLAVE
- Press Enter.
- The response should be OK, confirming the name change.
Step 3: Set the Role to Slave
- To assign the module the Slave role, type: AT+ROLE=0
- Press Enter.
- The module will respond with OK, confirming the role assignment.
Step 4: Set Connection Mode
- To set connection mode, type “AT+CMODE=0” and press Enter
- You should receive “OK” as a response.
Step 5: Retrieve the Module Address
- To get the module's unique address, type: AT+ADDR?
- Press Enter.
- The address will be displayed in hexadecimal format (e.g., 1234:56:7890AB).
- Note down this address, as it is required for configuring the Master module.
Step 6: Disconnect the Slave Module
- Once the configuration is complete, disconnect the USB cable from the PC/Laptop.
- Remove the Slave HC-05 module from the circuit to prevent interference during the Master configuration process.
The HC-05 module is now configured as a Slave and ready to pair with a Master module for communication.
Configuring the Bluetooth Module for the Master Role
Follow these steps to configure another HC-05 module for the Master role:
Step 1: Enter Command Mode
Connect the HC-05 module to the circuit, and place it into Command Mode the same way as done for the Slave module. The slow blinking LED confirms that the module is in Command Mode.
Step 2: Verify Communication
- Open the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.
- Type AT and press Enter.
- If the communication is successful, the module will respond with OK.
Step 3: Rename the Module
- To set the module's name, type: AT+NAME=MASTER
- Press Enter.
- The response OK confirms the name has been updated successfully.
Step 4: Assign the Role as Master
- To configure the module as the Master, type: AT+ROLE=1
- Press Enter.
- If successful, the module will reply with OK.
Step 5: Set Fixed Connection Mode
- To ensure the module connects to a specific address, type: AT+CMODE=0
- Press Enter.
- The module will respond with OK, indicating the connection mode is set to fixed.
Step 6: Pair the Master with the Slave
- Type the following command, replacing the address with the actual address of your Slave module:
- AT+BIND=0021,13,03BB60
- Replace 0021,13,03BB60 with the address of the Slave module.
- In this example, the Slave address is 21:13:3bb60.
- Press Enter.
- The module will respond with OK, confirming the pairing.
Step 7: Verify the Paired Address
- To check if the correct address is bound, type: AT+BIND?
- Press Enter.
- The response should display the bound address. If all zeroes or an incorrect address is displayed, repeat Step 6.
Step 8: Disconnect the Module
- Remove the USB cable from the PC/Laptop.
- Safely detach the Master HC-05 module from the circuit.
Your Master module is now configured and ready for communication with the Slave module.
Master-Slave Communication Between Two Arduino Boards Using HC-05 Bluetooth Modules

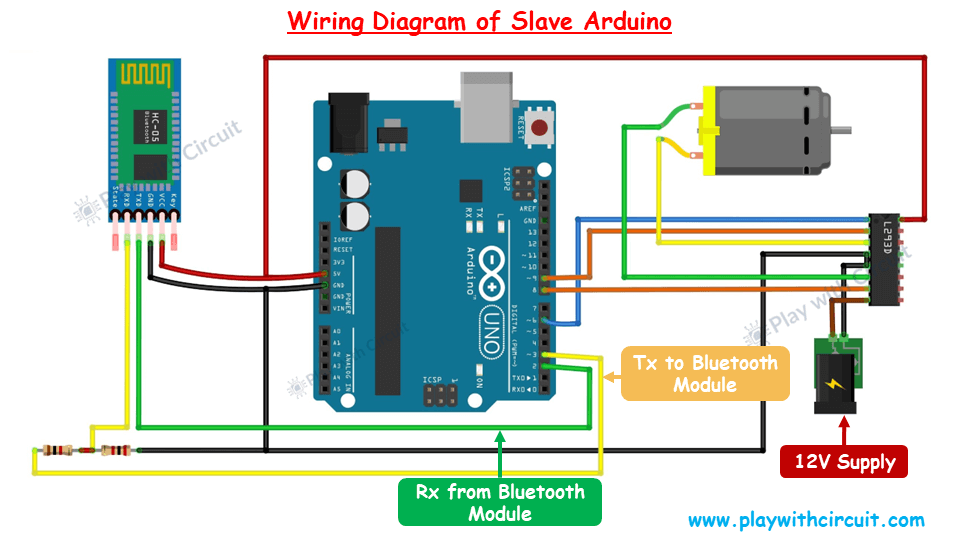
Now, let’s establish wireless communication between two Arduino UNO boards using the HC-05 Bluetooth modules.
We will set up two separate circuits: one for the Master device and another for the Slave device. The Master device will send commands to the Slave device, and the Slave device will execute the received commands and send a response back to the Master.
Master Arduino Code
This code allows the user to control the motor’s direction (clockwise or anticlockwise) and speed using buttons and a potentiometer connected to the Master Arduino.
Slave Arduino Code
This code is designed for the Slave Arduino that controls a motor (fan) using commands received from a Master Arduino via an HC-05 Bluetooth module.
To learn more checkout full article: Wireless Communication between two Arduino Boards using HC-05 Bluetooth Modules