NRF24L01 Bluetooth Servo Control
by ackasaurus in Circuits > Arduino
164 Views, 2 Favorites, 0 Comments
NRF24L01 Bluetooth Servo Control


Introduction
You will learn how to connect two Arduinos using Bluetooth in this instructable. To use Bluetooth, we will use two NRF sensors, one for each Arduino. Two potentiometers are used with the transmitter Arduino to control the two servos on the receiver Arduino.
What You Need
- Arduino Uno x2
- Servo x2
- Potentiometer x2
- NRF 24 x2
- Jumper Wires
- Breadboard x2
Wiring
Connect Bluetooth modules, servos and potentiometers.
Use a breadboard to create a ground and power terminal for each Arduino.
Connect each Arduino to a Bluetooth module using a breadboard
- · CSN - 8
- · CE - 9
- · MOSI - 11
- · MISO - 12
- · SCK - 13
Connect the servos to the receiver Arduino
Servo 1:
Ground - ground on Breadboard
Power - Power on Breadboard
Signal - 7
Repeat with Servo 2, but put the signal in Pin 6
Connect the potentiometers to the transmitter Arduino
Potentiometer 1:
VCC - power on breadboard
Signal - A0
GND - ground on breadboard
Repeat with Potentiometer 2, but put the input in A2
Full Wiring Diagram:
Install Libraries
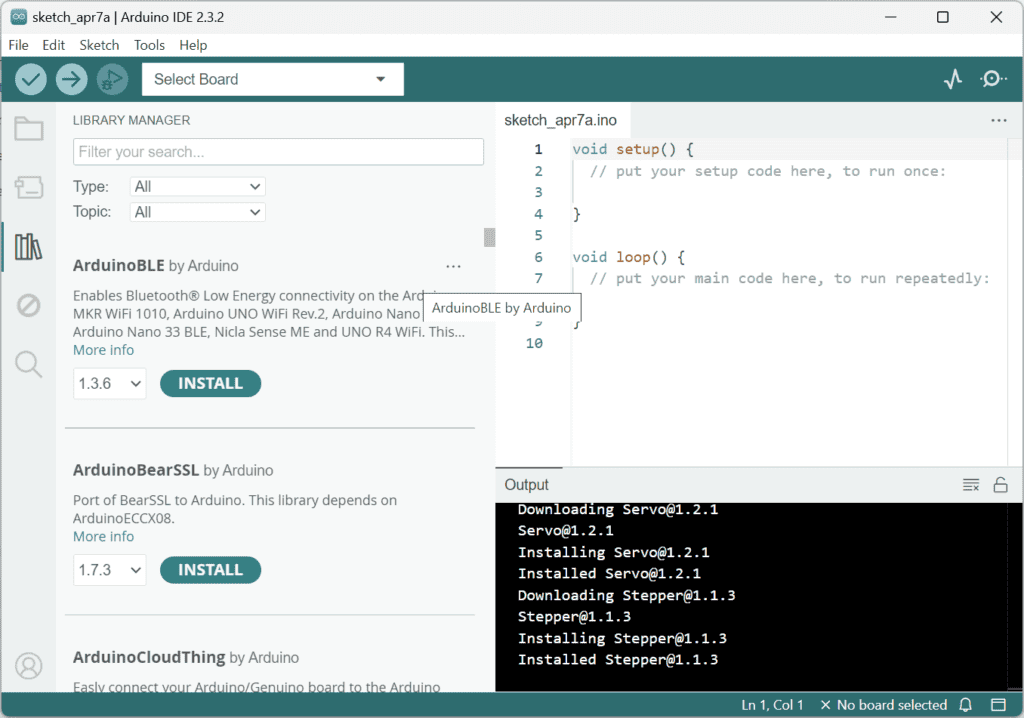
Install needed libraries
You will need to install libraries for the nRF modules to be used. It can be found directly in IDE. Install this library directly from the Arduino IDE Library Manager. Search for “rf24” and install the one by “TMRh20, Avamander”.
Install Code
Install code
Transmitter Code:
/ / add all relevant libraries
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
//declares CE, CSN pins
RF24 radio(9, 8); //(CE, CSN)
//declares analog pins for potentiometers
int potPin = A0;
int potPin2 = A2;
//declares the potentiometer value as an integer
int potValue = 0;
int potValue2 = 0;
//creates an array to hold 4 values
byte Array[4];
//Creates an address for two modules to communicate
const byte address[6] = "99150";
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
radio.begin();
//sets radio address
radio.openWritingPipe(address);
//declares Arduino as a Bluetooth transmitter
radio.stopListening();
}
void loop()
{
//stores analog(potentiomer 1) reading as an integer
potValue = analogRead(A0);
//Maps the potentiometer reading into degrees of motion for the servo to understand
potValue = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 179);
//sets elements of the arrays
Array[0] = 1;
Array[1] = potValue;
Array[2] = 3;
Array[3] = 4;
//Sends array over radio/Sends commands for servo 1
radio.write(&Array, sizeof(Array));
delay(1);
//stores analog(potentiomer 2) reading as an integer
potValue2 = analogRead(A2);
//Maps the potentiometer reading into degrees of motion for the servo to understand
potValue2 = map(potValue2, 0, 1023, 0, 179);
Array[0] = 2;
Array[1] = potValue2;
Array[2] = 6;
Array[3] = 8;
//Sends array over radio/Sends commands for servo 2
radio.write(&Array, sizeof(Array));
delay(1);
//prints servo position
Serial.println(potValue);
Serial.println(potValue2);
}
Receiver Code:
//include all relevant libraries
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
#include <Servo.h>
//declares CE, CSN pins
RF24 radio(9, 8); //(CE, CSN)
//declares the potentiometer value as an integer
int potValue = 0;
int potValue2 = 0;
//declares servos
Servo servo1;
Servo servo2;
//creates an address for two modules to communicate
const byte address[6] = "99150";
void setup()
{
//declares pins for servos
servo1.attach(7);
servo2.attach(6);
while (!Serial);
Serial.begin(9600);
radio.begin();
//sets radio address
radio.openReadingPipe(0, address);
//declares Arduino as receiver
radio.startListening();
}
void loop()
{
//reads data from Arduino if available
if (radio.available())
{
//holds incoming message
byte Array[4];
//reads message from other Arduino
radio.read(&Array, sizeof(Array));
//determines that the array is from potentiometer 1
if (Array[0] == 1)
{
potValue = Array[1];
//writes servo 1 value
servo1.write(potValue);}
//determines that the array is from potentiometer 2
if (Array[0] == 2)
{
potValue2 = Array[1];
//writes servo 1 value
servo2.write(potValue2); }
//prints servo position
Serial.println(potValue2);
Serial.println(potValue);
}
delay(10);
}